
Topology and Its Types
What is Topology?
Topology refers to the arrangement or arrangement of elements (such as devices, nodes, or computers) in a network. It describes how different network components are connected and how data flows between them.
Types of Topology
Topology can be categorized into two main types:
- Physical Topology – Refers to the actual physical arrangement of devices and cables in a network.
- Logical Topology – Describes how data moves within the network, regardless of the physical structure.
Common Types of Network Topologies
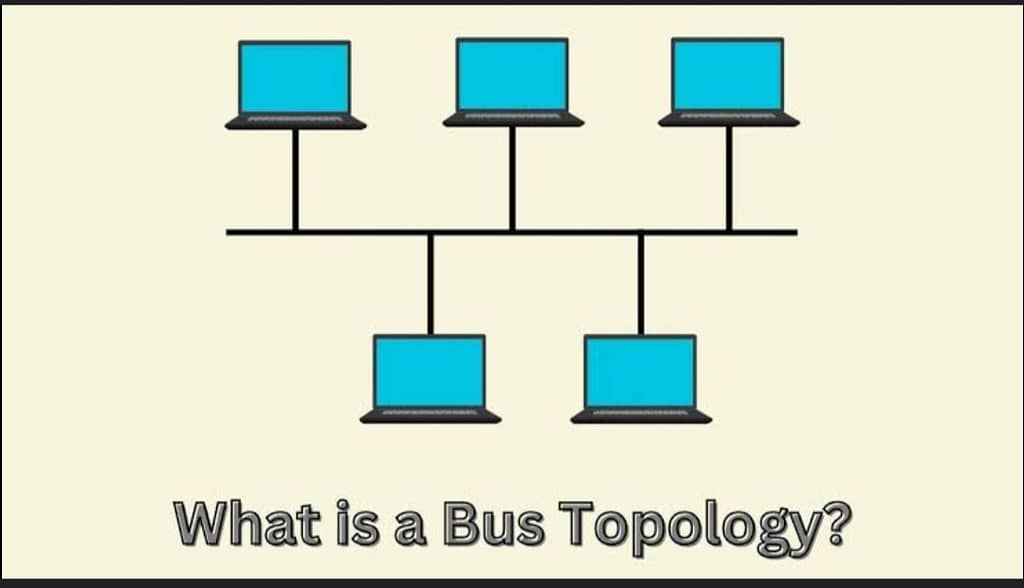
1️⃣ Bus Topology
- All devices are connected to a single central cable (backbone).
- Data travels in both directions along the cable.
- If the backbone fails, the entire network is affected.
✅ Advantages:
✔️ Easy to install and requires less cabling.
✔️ Cost-effective for small networks.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ If the main cable fails, the entire network goes down.
❌ Data collisions can occur when multiple devices communicate.
2️⃣ Star Topology
- All devices are connected to a central hub or switch.
- The hub/switch manages communication between nodes.
✅ Advantages:
✔️ Easy to add or remove devices.
✔️ If one device fails, the rest of the network remains operational.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ The central hub is a single point of failure.
❌ More cabling is required compared to bus topology.
3️⃣ Ring Topology
- Each device is connected to two other devices, forming a circular structure.
- Data travels in one direction (unidirectional) or both directions (bidirectional).
✅ Advantages:
✔️ No data collisions since data flows in a structured manner.
✔️ Predictable performance with consistent data transfer speeds.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ If one node or cable fails, the entire network may be disrupted.
❌ Difficult to troubleshoot and expand.

4️⃣ Mesh Topology
- Every device is connected to every other device.
- Two types: Full Mesh (all devices connected) and Partial Mesh (some devices connected).
✅ Advantages:
✔️ Highly reliable and fault-tolerant.
✔️ If one link fails, data can take another route.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ Expensive due to excessive cabling and connections.
❌ Complex to set up and maintain.

5️⃣ Tree (Hierarchical) Topology
- A combination of star and bus topologies.
- Has a parent-child structure with multiple levels.
✅ Advantages:
✔️ Scalable and easy to manage.
✔️ Suitable for large organizations.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ If the main backbone fails, the entire network is affected.
❌ Complex to set up compared to simpler topologies.
6️⃣ Hybrid Topology
- A combination of two or more different types of topologies.
- Used in large and complex networks.
✅ Advantages:
✔️ Flexible and scalable for different network needs.
✔️ Can be optimized for performance and reliability.
❌ Disadvantages:
❌ More expensive and complex to implement.
❌ Requires advanced network management.
Conclusion
The choice of topology depends on factors such as network size, cost, reliability, and scalability. Star topology is commonly used in modern networks due to its efficiency, while mesh topology is preferred for high security applications..

Leave a Reply